| |
|
|
| |
About
the Project >> Conservation
Issues |
|
| |
|
|
| |
Not long ago, cultivation of lac was carried practically
throughout the country. Though lac insects are found in the nature
all over the country, its cultivation is now restricted only to
Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh, and certain pockets of Madhya Pradesh,
Maharashtra and West Bengal. As a result, many species of lac
insects have either become extinct or are in the 'waiting list' of
extinction. With abandoning of lac cultivation, unutilised lac
hosts are frequently cut for timber and fuel wood etc. Out of more
than 400 plants on which lac insects have been observed, only
about two dozen are utilised for lac production as commercial lac
cultivation on other plants is economically not viable. Moreover,
lac-host plants exploited for commercial production of lac vary
from region to region. Danger looms large on other host-plants
whose economic importance remains to be realized.
Future of various flora and fauna associated with lac is thus,
intricately linked to the fate of lac cultivation. Fast shrinking
area of lac cultivation is a serious threat to the biodiversity of
lac insect ecosystem.
Some of the important issues at stake are:
-
Of the 26 species of lac insects reported from the country,
mainly Kerria lacca is exploited for commercial production of
lac. K. chinensis in the north-eastern states and K. sharda in
coastal regions of Orissa and West Bengal are also cultivated to
a certain extent. Potential of other lac insect species reported
from the country remains to be exploited. Wild lac insects are
principally distributed in the forest and sub-forest region
thus, the future of lac insects is intricately linked to the
fate of forests. Fast depleting forest cover of the country is a
serious threat to the bio-diversity of lac insects as well as
their host-plants. In the absence of human intervention, the
unattended species of lac insects and their host-plants might be
lost.
|
|
| |
 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
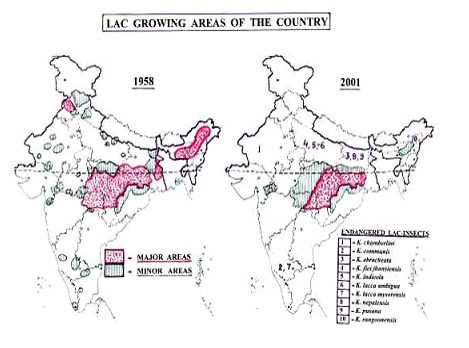
- Conversion of forest land for
agricultural and industrial activities has eroded the lac
cultivation area. Assam, Meghalaya, Orissa, Punjab and Uttar
Pradesh earlier contributed significantly in lac production but
now their share is almost negligible as cultivation of lac has
been abandoned. Many species of lac insects reported from these
places have thus, become endangered.
|
|
| |

Lac infestation on Litchi at Ranchi
(Jharkhand) |
 |
 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
- Lac insects infesting
economically important plants, viz., litchi (Litchi chinensis),
mango (Mangifera indica), ber (Ziziphus mauritiana), sandal (Santalum
album) etc. are the direct target of pest management leading to
erosion of the biodiversity of lac insects and associated fauna.
- Lac insect species belonging
to Paratachardina genus do not produce true lac of commercial
importance and are pests of such important plants as sandal (S.
album) and tea (Thea chinensis) and hence, are deliberately
destroyed.
- Some of the insect fauna
associated with the lac insects are species-specific (exclusive
to the ecosystem) and hence, loss of even one species of lac
insect poses a danger of losing many other related species.
- In agriculturally advanced
states like Punjab and Haryana, ber (Z. mauritiana) in the wild
has been replaced by high yielding fruit varieties. The trees
are regularly pruned and subjected to pest management measures,
which have led to the loss of lac insects.
- In drought prone states like
Rajasthan and Gujarat, twigs of lac host trees such as palas (Butea
monosperma), rain tree (Albizia saman) and Ficus spp. are
utilized as cattle fodder during adverse conditions, thus
preventing natural multiplication of lac insect populations.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
QUICK LINKS |
|
|
| |
Contact Us |
Contact
Network Centres |
|
Role of
Network Centres |
Email
address |
|
Copyright @ 2014 Indian
Institute of Natural Resins & Gums (ICAR), Ranchi - 834 010, INDIA |
|



